As the global demand for energy storage continues to surge, the battery industry has witnessed remarkable growth. This expansion, however, has necessitated the development and implementation of robust regulations to address various aspects, including battery manufacturing, the battery supply chain, and the extraction of battery materials. Such regulations play a vital role in ensuring the safe and sustainable production, distribution, and disposal of batteries while striving to minimize environmental impact and safeguard public health. This guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the intricate world of battery regulations, highlighting real-world examples and key considerations.
The extraction of battery materials is a complex and often environmentally damaging process. In order to protect the environment and ensure that the extraction of battery materials is carried out in a sustainable manner, a number of regulations have been put in place.
One of the most important regulations is the European Union’s Batteries Regulation. This regulation sets out several requirements for extracting, processing and using battery materials. For example, the regulation requires that battery manufacturers use recycled materials whenever possible and that they minimize the environmental impact of their operations.
The United States also has several regulations governing the extraction of battery materials. These regulations are enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The EPA regulates the use of hazardous chemicals in the extraction process and requires that companies minimize the amount of waste they produce.
In addition to government regulations, a number of non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are working to promote sustainable battery production. These NGOs are working to raise awareness of battery production’s environmental and social impacts and encourage companies to adopt more sustainable practices.
The extraction of battery materials is a critical part of the transition to a clean energy future. However, it is important to ensure that this process is carried out in a sustainable manner. The regulations that are currently in place are a good start, but more needs to be done to protect the environment and ensure that the extraction of battery materials is carried out in a responsible manner.
Here are some of the key provisions of the Extraction of Battery Materials Regulations:
These regulations are designed to protect the environment and ensure that the extraction of battery materials is carried out in a sustainable manner. By complying with these regulations, companies can help to ensure that the transition to a clean energy future is done in a responsible manner.
Supply chain regulations govern the sourcing of battery materials, including the mining, processing, and transportation of these materials. They aim to ensure that battery materials are sourced in a sustainable and responsible manner and that the workers involved in the supply chain are treated fairly.
One of the most important aspects of battery supply chain regulation is the use of conflict minerals. Conflict minerals are minerals extracted in conflict-affected areas, and their trade can help finance armed conflict. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 requires companies to disclose whether their products contain conflict minerals and to take steps to ensure that these minerals are not sourced from conflict-affected areas.
Another important aspect of battery supply chain regulation is the use of child labour. Child labour is the employment of children under the age of 18 in hazardous or exploitative conditions. The International Labour Organization (ILO) has adopted a number of conventions that prohibit child labour, and many countries have laws that ban or restrict the employment of children. Battery companies are subject to these laws, and they must take steps to ensure that their products are not made with child labour.
There are several different supply chain regulations related to battery manufacturing. These regulations vary from country to country, but they typically include requirements for companies to:
Some of the most important supply chain regulations related to battery manufacturing include:
By complying with these regulations, battery companies can help ensure that batteries are produced sustainably and responsibly.
In addition here are some relevant regulations:
1. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 requires companies to disclose whether their products contain conflict minerals. Conflict minerals are minerals extracted in conflict-affected areas, and their trade can help finance armed conflict. The law also requires companies to take steps to ensure that these minerals are not sourced from conflict-affected areas.
2. The European Union’s Conflict Minerals Regulation
The European Union’s Conflict Minerals Regulation is similar to the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010. It requires companies that sell products in the European Union to disclose whether their products contain conflict minerals and to take steps to ensure that these minerals are not sourced from conflict-affected areas.
3. The Responsible Minerals Initiative
The Responsible Minerals Initiative is a global initiative that aims to improve the sustainability of the mining and supply chain for conflict-free tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold. The initiative works with companies, governments, and civil society organizations to develop and implement responsible sourcing practices.
4. The Fair Cobalt Alliance
The Fair Cobalt Alliance is a global initiative that aims to improve cobalt miners’ working conditions and human rights. The alliance works with companies, governments, and civil society organizations to develop and implement fair labour practices in the cobalt mining industry.
5. The Battery Industry Climate Action Partnership
The Battery Industry Climate Action Partnership is a global initiative that aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the battery industry. The partnership works with companies, governments, and civil society organizations to develop and implement technologies and practices that reduce battery production’s environmental impact.
By complying with these regulations and participating in these initiatives, battery companies can help ensure that batteries are produced sustainably and responsibly.
The manufacturing of batteries can also have a significant impact on the environment. For example, the production of lithium-ion batteries requires the use of hazardous chemicals, and the disposal of these batteries can release these chemicals into the environment. Battery companies are subject to environmental regulations that aim to minimize the environmental impact of battery manufacturing.
These regulations can include requirements for companies to use environmentally friendly manufacturing processes, recycle hazardous materials, and dispose of batteries in an environmentally friendly manner. Below are a few examples of the regulations relating to battery manufacturing.
Safety and Performance Standards: Battery manufacturing involves numerous intricate processes that require strict adherence to safety and performance standards. Regulations within battery manufacturing aim to ensure the quality, reliability, and safety of battery products. These regulations encompass guidelines for materials selection, manufacturing processes, testing procedures, and quality control measures.
Manufacturing Processes: Regulations governing battery manufacturing processes encompass various aspects, including electrode fabrication, cell assembly, and module integration. These regulations often specify manufacturing standards, process controls, and quality assurance measures to ensure consistent and safe production. For example, the International Electrotechnical Commission’s (IEC) standards, such as IEC 62660, provide guidelines for lithium-ion battery manufacturing, covering aspects like cell design, electrical performance, and safety testing.
Testing and Quality Control: Battery regulations necessitate comprehensive testing and quality control procedures throughout the manufacturing process. These regulations define test methodologies, performance criteria, and safety requirements for batteries. Manufacturers must conduct rigorous testing, including electrical performance testing, environmental testing (e.g., temperature, humidity, vibration), and safety testing (e.g., impact resistance, thermal stability). Compliance with standards such as the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria for Lithium Batteries ensures the safe transportation of batteries.
Worker Safety and Occupational Health: Battery manufacturing regulations prioritize worker safety and occupational health within production facilities. These regulations establish guidelines for safe working conditions, personal protective equipment (PPE), and handling protocols to protect workers from potential hazards associated with battery manufacturing processes.
Hazardous Materials Handling: Battery manufacturing often involves the use of hazardous materials, including corrosive electrolytes and flammable substances. Regulations mandate appropriate handling procedures, storage requirements, and waste management practices for these materials to safeguard workers’ health and minimize environmental risks. Compliance with regulations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA) Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) ensures proper labelling, handling, and communication of hazardous materials within manufacturing facilities.
Battery regulations can help to protect the environment and improve safety. They can also promote innovation in battery technology. However, there are a number of challenges and obstacles to the implementation of battery regulations. These challenges include:
Despite these challenges, there are a number of reasons why battery regulations are important. Battery regulations can help to:
As the demand for batteries continues to grow, it is likely that battery regulations will become more stringent. This is necessary to ensure that batteries are produced and used in a safe and environmentally responsible manner.
Here are some of the ways to overcome these challenges:
By addressing these challenges, countries can help to ensure that battery regulations are effective in protecting the environment and promoting innovation.
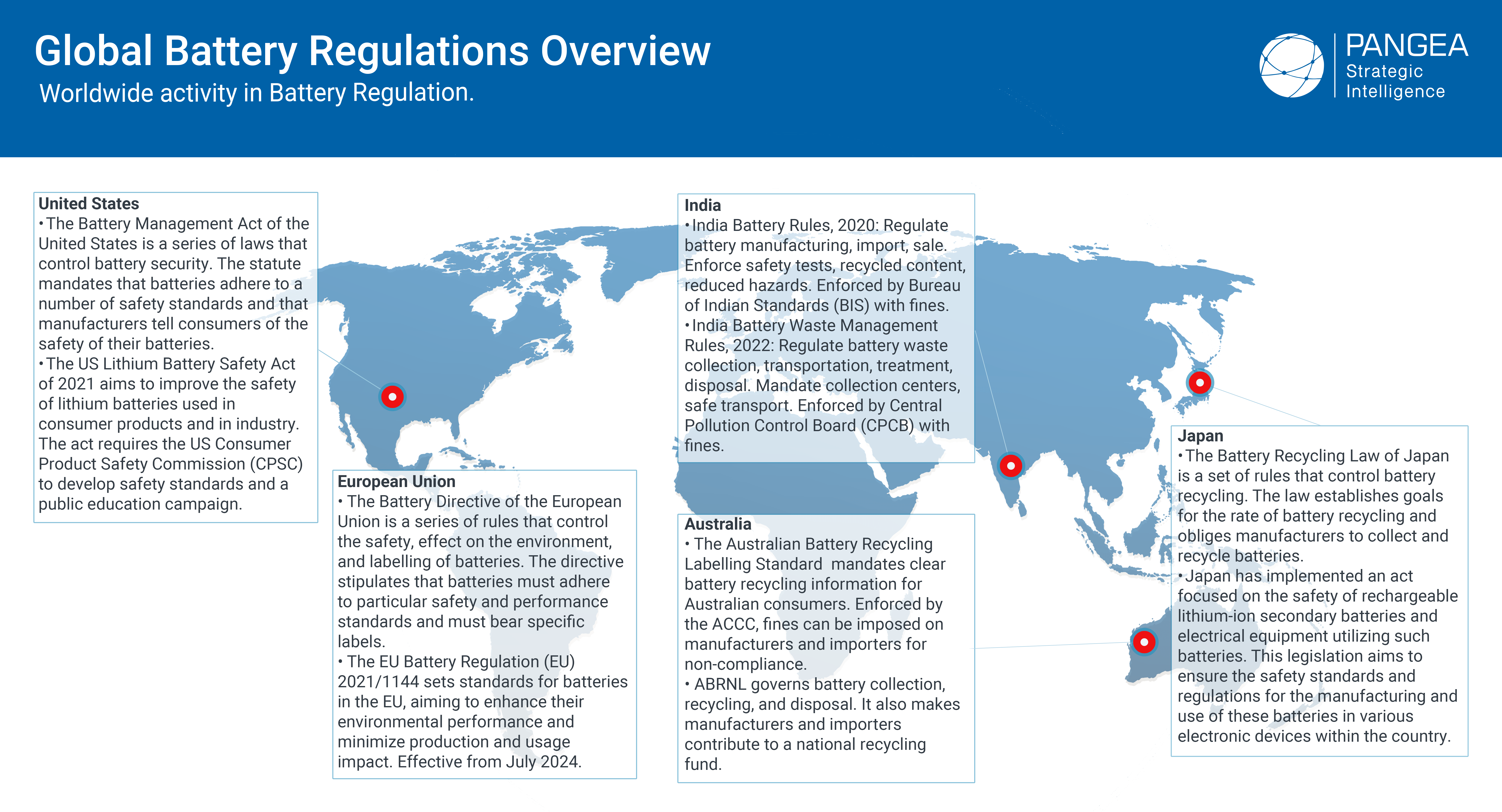
In addition to regulations, there are also a number of voluntary initiatives that battery companies can participate in. These initiatives can help to improve the sustainability of the battery supply chain and manufacturing process.
Some of the most important voluntary initiatives include the Responsible Minerals Initiative, the Fair Cobalt Alliance, and the Battery Industry Climate Action Partnership.
The Responsible Minerals Initiative is a global initiative that aims to improve the sustainability of the mining and supply chain for conflict-free tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold. The Fair Cobalt Alliance is a global initiative that aims to improve cobalt miners’ working conditions and human rights. The Battery Industry Climate Action Partnership is a global initiative that aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the battery industry.
By complying with regulations and participating in voluntary initiatives, battery companies can help ensure that batteries are produced and used sustainably and responsibly.
Batteries are essential for a wide range of products, and the demand for batteries is growing. As the demand for batteries grows, so does the need for regulations to ensure that they are produced and used in a sustainable and responsible manner.
The dynamic nature of the battery industry necessitates a continuously evolving regulatory landscape. By examining real-world examples and exploring the challenges and opportunities within battery regulation, we gain valuable insights to promote the safe, sustainable, and responsible development of battery technologies.
There are several different battery regulations in place around the world, and there are also a number of voluntary initiatives that battery companies can participate in. By complying with regulations and participating in voluntary initiatives, battery companies can help ensure that batteries are produced, used and recycled, sustainably and responsibly.
You can register for free. It is quick and easy and once registered you will get full access to all our premium content.
Just log in and learn, then absorb content covering: