The main commercial uses of electrolysers:
An electrolyser is a chemical system/process that breaks water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. This process is called electrolysis. Hydrogen is set to be at the front of the energy transition and leading the shift to a greener world. Electrolysis is the production method for this and has sparked the rising demand for electrolyser technology.
Electrolysers do have multiple applications across different sectors. Most of the electrolyser activity relates to hydrogen production due to its key involvement in the energy transition. When electrolysis is powered by renewable energy, green hydrogen is produced.
However, this is not the only use for electrolyser technology:
For example, copper extracted from its ore is 98% to 99% pure and has high resistivity. However, copper that’s required for electrical applications must have a minimum purity of 99.92%. This refining process allows having copper that has a purity of over 99.92% to be applicable for electrical appliances.
Many other metals such as zinc and aluminium are purified and refined using electrolysis.
To electroplate an object, it must first be cleaned, degreased, and arranged as a cathode in a voltammeter containing anode and electrolyte of the metal to be deposited. In order to have an even layer, it must be surrounded by a set of anodes or rotated at a steady speed. This then helps to provide an even and smooth layer.
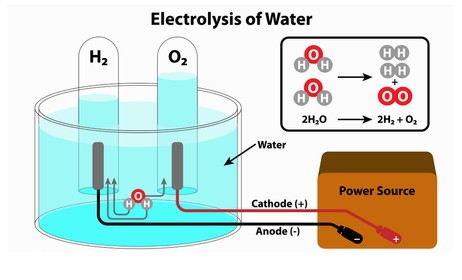
Electrolysis is carving the way for hydrogen production to achieve the Hydrogen Energy Earthshot goal of reducing the cost of clean hydrogen by 80% to $1 per 1 kilogram in 1 decade. The electrolysis process requires high levels of electricity and when analysing the benefits and economic viability of hydrogen production via electrolysis, electricity source, costs, efficiency, and emissions from electricity generation must all be considered.
As it stands today, power grids around the world are not set up for providing the electricity required for electrolysis to produce green hydrogen. This is due to the current lack of renewable energy sources available. Therefore, the production of hydrogen by renewable options (wind, solar, geothermal) is being highly pursued. These options would allow for a zero-emissions process, but currently, costs need to decrease across the chain to make this a competitive and commercially viable process.
In addition, electrolyser technology for hydrogen production can have synergy with renewable energy generation. Although the costs of renewable technologies such as wind are continuing to drop, the wind is a variable factor and is a limiting factor for wind energy. If electrolysers and hydrogen production was integrated into wind farms it would allow flexibility to run at the optimum capacity at all times. And in times of excess electricity production by wind, rather than wasting energy it could be used in the electrolysers to allow for further hydrogen production.
Lastly, there is a constantly growing demand for fuel cell-based vehicles. This ever-rising demand for fuel cell-based vehicles such as EVs across mainly North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific is set to be a boost in the demand for electrolysers. Hydrogen can store vast amounts of energy which is able to be released when required. Hydrogen based vehicles are a possibility for the automotive sector, with companies like Audi and Hyundai working together to research and develop a hydrogen car. The need for a green shift in the automotive sector will open another gap where electrolysers will be essential.

Although electrolysers are an amazing technology with many applications and are sure to become a key link in the hydrogen production chain. There are challenges and it is important to note they are not perfect.
Currently, the electricity grids around the world are not built for electrolysers. Most of the current electricity is generated using fossil fuels. This means as it stands a lot of hydrogen produced using electrolysis would not actually be green hydrogen.
Renewable energy technologies are growing, and the current electricity grid will become more renewable weighted. However, currently, the best option is using a renewable energy source that is separate from the main grid. This is not a long-term solution however and is a limitation for our hydrogen production and the use of electrolysers.
The U.S. Department of Energy and other governments and organisations around the world are continuing to try and bring down the cost of renewable-based electricity production and develop more efficient fossil-fuel-based electricity production with carbon capture, utilisation, and storage.
Another consideration of electrolysers is, as it stands, they require huge amounts of energy to power and can be highly costly to run. Some experts have said that due to the energy electrolysis requires, it may not be commercially and economically viable in the long term.
Hydrogen costs around $12 per kilogram, far more than gas and oil. Currently, user electrolysers such as the alkaline electrolyser require 45kWH per kg of hydrogen produced. This is a much higher energy consumption than many alternative energy sources and much hamper the market. But new technologies such as the PEM device aim to overcome these challenges and could help to drive the market forward.