The first nuclear chain reaction was carried out under a stadium at the University of Chicago in 1942 by physicist Enrico Fermi. What followed, were a series of milestones leading to the first nuclear powerplant in the former Soviet Union in 1954.
There are two different ways that we can make use of the energy from nuclear reactions. The first is called a boiling water reactor that uses the heat energy to directly turn water into steam which is then directed to power a turbine generator.
The second method, a pressurized nuclear reactor, is different since the water that is initially heated is pressurized enough to stay as a liquid. The reactor reaches very high temperatures. Which then heats a separate body of water and, in turn, follows the same process as the boiling water reactor. The benefit of this method, as opposed to the boiling water reactor, is that it is much safer. There is less fissile material needed, and as the heat increases, it is also easier to control as it produces less power.
The main attraction of nuclear energy is that it is entirely clean. It produces zero greenhouse gasses whilst producing incredible amounts of power. Compared to other green energy sources, it would take more than 3 million solar panels or 430 wind turbines to produce the same amount of energy as a nuclear reactor.
Nuclear fuel is also incredibly energy dense. A single uranium pellet is just an inch tall. This tiny energy source is capable of producing the same amount of energy as 120 gallons of oil or 17,000 cubic feet of natural gas. Meaning that while materials like uranium are rare and high cost, the energy output is more than enough to justify their use.
An added benefit is that a typical nuclear facility needs around 1 square mile to function correctly, while a wind farm would need 360 times that to have the same energy output. However, a nuclear facility is often situated near large bodies of water, as substantial amounts of clean water are required for this process to work effectively and safely.
While nuclear energy is clean, it is not renewable. The fuel is 96% fissile even after being used. The 4% remaining has to be condensed and stored underground for 500 years before the radioactivity becomes safe to be around. While 4% is not a huge portion to be wasteful, it doesn’t change that the fuel behind nuclear energy is finite and will eventually run out. with consistent usage, making recycling paramount to getting the most from nuclear energy.
Nuclear energy also carries a stigma from the unfortunate legacy of the Chornobyl and Fukushima incidents. Due to the incidents, creating nuclear infrastructure often comes with a strong public reaction from locals and activists that would aim to stop its creation. Fortunately, in recent times there have been strides in rebranding nuclear energy as an incredible achievement. Nuclear energy may be the face of cleaner energy in the future. While not entirely avoiding the issue, it is a step towards public acceptance of nuclear energy.
A great example of how to utilize nuclear energy would be Ukraine. The four nuclear power plants in the country supply 21% of all the energy the country needs. While their primary energy source is natural gas, for just four stations to create a fifth of their energy is still an astounding figure.
The unfortunate point of discussion for Ukraine is the Chornobyl disaster. The 1986 incident reflected poorly on the future of nuclear energy. However, since then, there have been advances in safety and training to ensure that the Chornobyl incident would not happen again. This was recently proven, by a missile strike from Russia that caused the second biggest nuclear plant in Ukraine to be disconnected from the national electricity grid. New safety measures were put in place to make sure they could react promptly to a power outage. It ensures that another meltdown is highly unlikely and the station can remain to function.
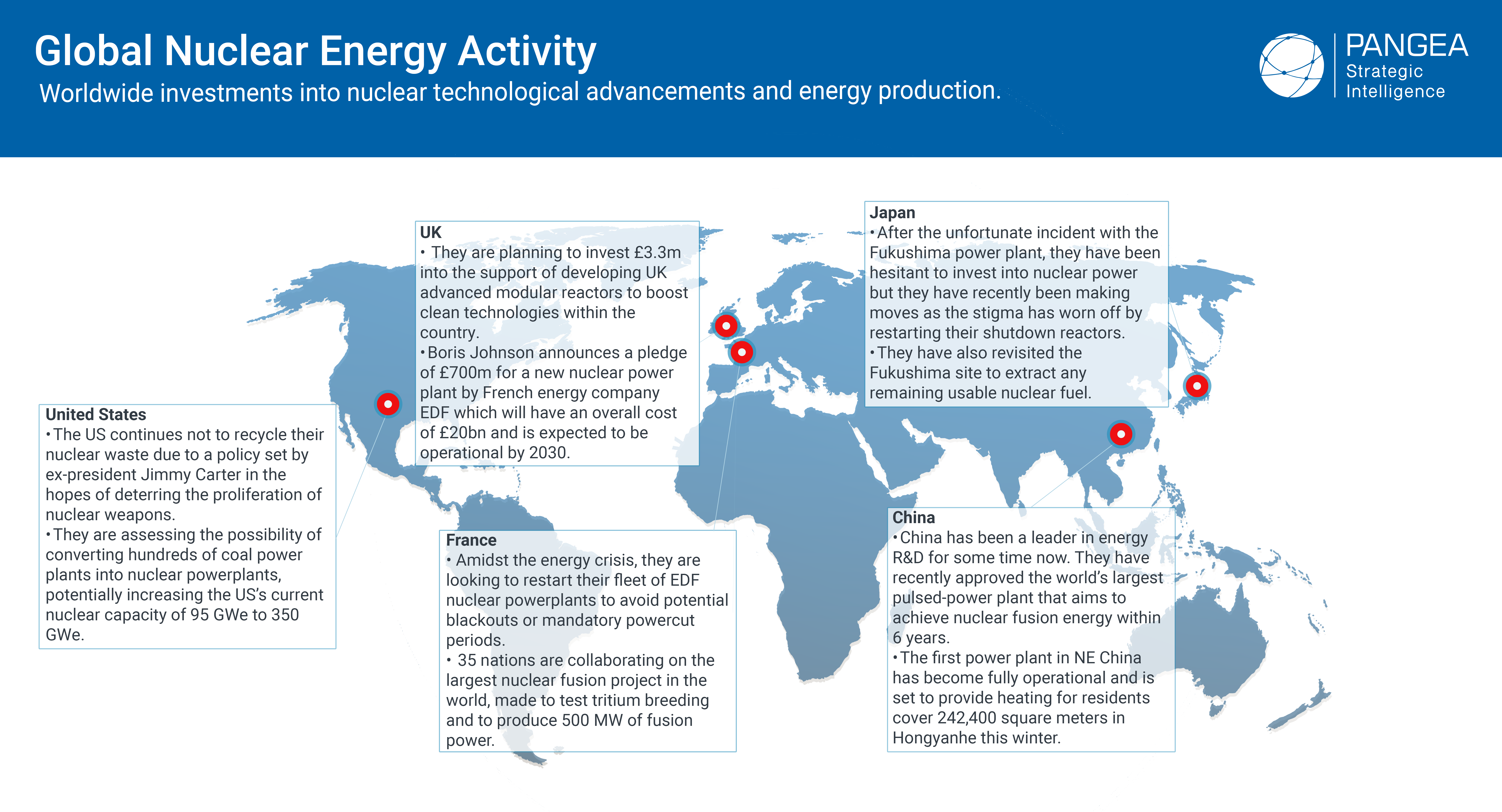
| France 70% of the energy in France is produced by nuclear power stations: 17% of which is from recycled material. They have 56 functioning nuclear reactors that have a joint capacity of 61,370 MWe. |
United States Its the largest producer of nuclear power accounting for 30% of worldwide production. The country holds 92 operating nuclear reactors, with a capacity of 94,718 MWe, which generates 20% of the country’s electricity. Unfortunately, they are not yet recycling their used nuclear fuel. |
| China China is particularly nuclear motivated due to the air pollution issue. Their 54 nuclear power plants have a capacity of 52,150 MWe which accounts for nearly 5% of the power usage. They are expanding their nuclear power through a closed nuclear fuel cycle. |
Japan Before the Fukushima incident, there were ambitious plans to have nuclear energy make up 40% of their usage by 2017, now they are looking for 20% by 2030. They currently have 30 nuclear reactors operating, with a capacity of 31,679 MWe, and 16 more waiting for approval to restart. |
| Russia Is one of the leaders in the progression of harnessing nuclear energy, dedicated to closing its fuel cycle. They have 37 operating nuclear reactors with a capacity of 27,727 MWe. Nuclear energy accounts for 20% of the country’s used power. |
✓ How is the worldwide market for nuclear coolants?
✓ How can fusion reactors fit within your project?
✓ What are the standards and policies needed for your project?
✓ What are the right investments to make in clean energy?
Clients notify us that they need leading insight for their project.
We engage and vet subject matter Experts matched to the request at speed.
Clients consult with their shortlisted Expert(s) and obtain forward knowledge to incorporate into their strategic plans.
Clients benefit from more refined analysis and practical guidance to achieve a quantifiable business impact.