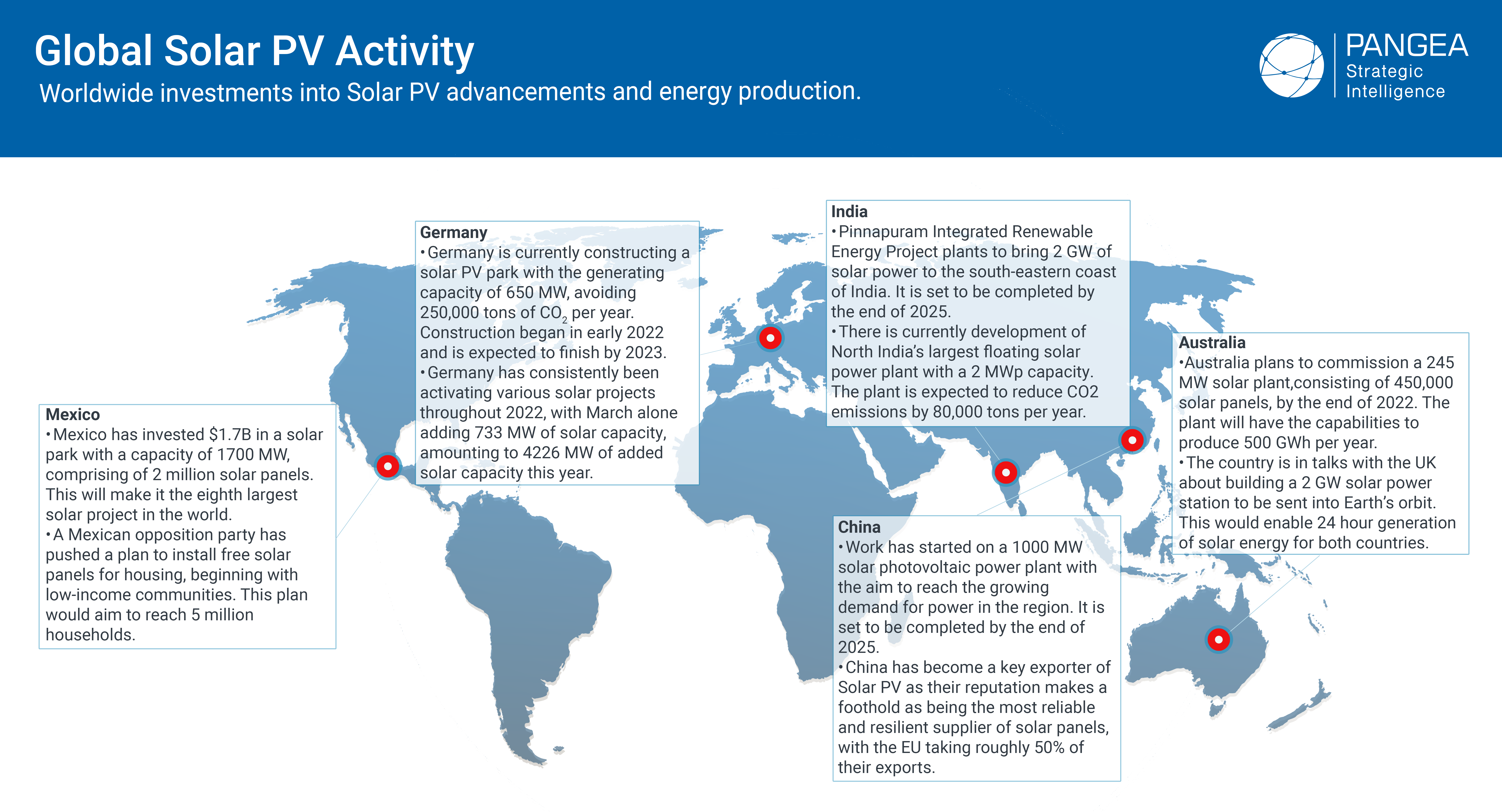
As well as governments embracing Solar power, more and more companies worldwide are investing in the power that Solar PV can bring. According to The Carbon Majors Database, only around 100 of the thousands of companies in the world are responsible for 71% of global greenhouse gas emissions since 1998. As well as the environmental benefits that solar PV can bring, financial gains can be achieved, by producing your own power you’re saving money that would otherwise go to energy corporations. Some examples of companies already taking the plunge into Solar Power are:
1) Walmart – 89.43MW – 215 sites (335 globally)
2) Costco – 47.06MW – 78 sites
3) Kohl’s – 47MW – 156 sites
4) Apple – 40.73MW – 5 sites
5) Ikea – 35.08MW – 39 sites
The International Energy Agency Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme (IEA PVPS) estimates that 173.5 GW of new solar capacity was installed in 2021, and that figure might rise to 260 GW in 2022. As for Solar PV generation, they have predicted that it has increased by a record 179 TWh (up 22%) in 2021 to exceed 1 000 TWh. It demonstrated the second-largest absolute generation growth of all renewable technologies in 2021, after wind. However, to achieve the world’s net zero emissions scenario, then the average annual growth for Solar PV will need to be at 25% per annum, during the period of 2022-2030. This is reflected in the graph below.
Solar Power and Solar PV have come a long way since their creation in 1954, with cells being made that are stronger/longer lasting, panels that are more powerful and solar panels that can be printed onto other surfaces.
Rooftop PV is an electricity-generating photovoltaic system, mounted on the rooftops of commercial and residential buildings or structures. They can often reach a capacity of 100 KW to 1 MW and large roofs can generate up to 1-10 MW of solar power. The rooftop PV systems are small compared to large-scale solar PV farms due to their power output. There are financial benefits to Rooftop PV, with Installers having the right to feed solar electricity into the public grid, for a financial gain.
Because solar panels are never perfect, they will never be able to harness 100% of the sun’s energy. In fact, in the past, they were only able to generate around 20%, however, due to advancements, that number is now around a 31% conversion rate when converting solar energy to electrical current. Further advancements could revolutionize solar power generation and ultimately increase that conversion rate further.
A solar window is essentially a window with a solar panel inside, they feature a layer of photovoltaic glazing which converts sunlight into renewable electricity. They are still considered to be in their research stage, but solar experts say they will be available in the next 5 years. With certain advancements in solar windows, efficiency levels of between 12% and 15% are being achieved.
Silicon panels are becoming cheaper and more efficient by the day, and experts are turning to large bodies of water and making floating solar farms. The main benefits of floating farms are that they don’t take up any land, as well as the cooling nature of the water helps to produce up to 10% more power. However, the costs for a floating system are 20-25% higher than for a ground mounted.
In recent years the cost of Solar energy systems has been massively reduced. In the early 2000’s the price of solar power was around $10 per watt, nowadays that price has fallen to $0.10 per kWh and because of this, they are becoming more and more common in everyday households. The IEA estimates solar systems to supply 5% of global electricity consumption in 2030, rising to 16% by 2050. In order to achieve this vision, would require the global capacity of solar energy to increase from 150 gigawatts in 2014 to 4,600 gigawatts by 2050. The IEA states: “Solar PV is becoming the lowest-cost option for new electricity generation in most of the world, which is expected to propel investment in the coming years.”
| China China is the largest producer in the world of both photovoltaics and solar thermal energy. The country produces 27% of its energy from renewable resources and has reached a solar energy capacity of 300GW in 2021. |
United States In 2021, the United States had over 212GW of installed Solar PV power capacity. By 2015 Solar power had overtaken the oil, gas and coal industries for the highest employment rate. The oldest solar power plant in the world is a 354-megawatt located in California. |
| Japan Japan is 3rd in the world for Installed PV capacity, coming in with a capacity of around 74GW in 2021. Japan set 2 targets in 2004 and 2009 respectively, 28 GW of solar PV capacity by 2020 and 53 GW of solar PV capacity by 2030. The targets set for 2020 were surpassed in 2014, and the target for 2030 was surpassed in 2018. |
India The solar power industry in India is growing at a rapid rate. In 2021, India recorded around 60GW of solar power generated. The Indian government originally set an initial target of 20 GW capacity for 2022, which was achieved four years ahead of schedule. |
Clients notify us that they need leading insight for their project.
We engage and vet subject matter Experts matched to the request at speed.
Clients consult with their shortlisted Expert(s) and obtain forward knowledge to incorporate into their strategic plans.
Clients benefit from more refined analysis and practical guidance to achieve a quantifiable business impact.